SAT阅读必备可汗学院资料Part 1 Level 2 Passage5
2017/3/1 20:43:16来源:互联网作者:上海新航道
摘要:SAT阅读必备可汗学院资料Part 1 Level 2 Passage5!下面是小编为大家整理的电子版的SAT阅读必备可汗学院资料Part 1 Level 2 Passage5。Science相关的练习内容,大家可以打印下来方便学习。
SAT阅读必备可汗学院资料Part 1 Level 2 Passage5!下面是小编为大家整理的电子版的SAT阅读必备可汗学院资料Part 1 Level 2 Passage5。Science相关的练习内容,大家可以打印下来方便学习。
Questions 1-11 are based on the following
passage.
Adapted from Abi Berger, ”Magnetic Resonance Imaging,”
2002 by Abi berger.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses the body’s natural magnetic properties to produce detailed images from any part of the body. For imaging purposes the hydrogen nucleus (a single proton) is used because of its abundance in water and fat. The hydrogen proton can be likened to the planet earth, spinning on its axis, with a north-south pole. In this respect it behaves like a small bar magnet. Under normal circumstances, these hydrogen proton “bar magnets” spin in the body with their axes randomly aligned. When the body is placed in a strong magnetic field, such as an MRI scanner, the proton’s axes all lined up. This uniform alignment creates a magnetic vector oriented along the axis of the MRI scanner. MRI scanners come in different field strengths, usually between 0.5 and 1.5 tesla.
The strength of the magnetic field can be altered electronically from head to toe using a series of gradient electric coils, and, by alerting the local magnetic field by these small increments different slices of the body will resonate as different frequencies are applied. When the radiofrequency source is switched off the magnetic vector returns to its resting state, and this causes a signal (also a radio wave) to be emitted.It is this signal which is used to create the MR images. Receiver coils are used around the body part in question to act as aerials to improve the detection of the emitted signal. The intensity of the received signal is then plotted on a grey scale and cross sectional images are built up. Multiple transmitted radiofrequency pulses can be used in sequence to emphasis particular tissues orabnormalities. A different emphasis occurs because different tissues relax at different rates when the transmitted radiofrequency pulse is switched off. The time taken for the protons to fully relax is measured in two ways.The first is the time taken for the magnetic vector to return to its resting state and the second is the time needed for the axial spin to return to its resting state. The first is called T1 relaxation, the second is called T2 relaxation. An MR examination is thus made up of a series of pulse sequences. Different tissues (such as fat and water) have different relaxation times and can be identified separately. By using a “fat suppression” pulse sequence, for example,the signal from fat will be removed, leaving only the signal from any abnormalities lying within it.
Most diseases manifest themselves by an increase in water content, so MRI is a sensitive test for the detection of disease. The exact nature of the pathology can be more difficult to ascertain: for example, infection and tumor can in some cases look similar. A careful analysis of the images by a radiologist will often yield the correct answer. There are no known biological hazards of MRI because, unlike x ray and computed tomography, MRI uses radiation in the radiofrequency range which is found all around us and does not damage tissue as it passes through. *God help those who help themselves. We help those who trust us. Contact Wechat:satxbs123, help is waiting.
Magnetic Vector (T1) and Axial Spin (T2) Relaxation Times for Different Molecules/Tissues, in Milliseconds
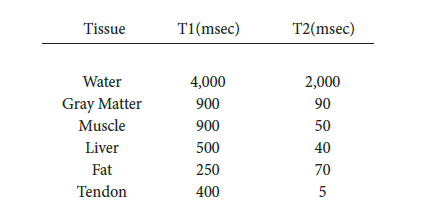
Source: Data from Bottomley PA, et al. “A Review of Normal Tissue Hydrogen NMR Relaxation Times and Relaxation Mechanisms from 1-100 MHz: Dependence on Tissue Type, NMR Frequency, Temperature, Species, Exision, and age.” Med Phys 1984; 11: 425-448 Science
4Over the course of the passage, the main focus shifts fromA) an explanation of how magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) works to a discussion of MRI’s practical advantages.
B) a story about the origin of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to a discussion of alternative imaging methods used by scientists.
C) an explanation of tissue relaxation rates to a summary of the magnetic properties of hydrogen protons.
D) an introduction about the properties of radiofrequency waves to a criticism of the health risks of x-ray devices.
5 The “planet earth” image in line 6-7 mainly serves to A) highlight an unlikely parallel between the fields of biology and astronomy.
B) inject a note of humor into an otherwise serious explanation of magnetic resonance imaging.
C) create a pun centered on the idea that hydrogen is necessary for life on this planet.
D) communicate a complex scientific idea using a more familiar concept.
6It can reasonably inferred from the passage that electromagnetic waves in the radio frequency range
A) do not create long-lasting effects on the human body.
B) only create magnetic fields in tissues with high water content.
C) are stronger than waves in the x-ray range.
D) always travel in the same direction.
1 Which choice best reflects the author’s point of view regarding magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)?
A) It is the most important tool used by scientists to aid in the diagnosis of particular diseases.
B) It is a valuable and effective technique but should be used sparingly in order to prevent possible
damage to the body.
C) It is a breakthrough technology that will revolutionize the treatment of particular ailments.
D) It is a useful tool in disease diagnosis,although specialized training is required to accurately interpret MRI images.
Which choice provides the best evidence for the answer to the precious question?
A) lines 17-21 (“The strength...applied”)
B) lines 30-34 (“Multiple...off ”)
C) lines 42-47 (“Different...it”)
D) lines 48-54 (“Most...answer”)
It can reasonably be inferred from the passage that, like a bar magnet, the nucleus of a hydrogen atom
A) spins in a counter-clockwise direction.
B) is responsive to external magnetism.
C) attracts metallic substances.
D) is surrounded by electrons.
Which choices provides the best evidence for the answer to the previous question?
A) lines 22-24 (“When...emitted”)
B) lines 28-29 (“The...up”)
C) lines 34-39 (“The time...state”)
D) lines 55-59 (“There...through”)
8 As used in line 49, "sensitive" most nearly means
A) appreciative
B) unstable
C) discerning
D) observant
9The data in the table support the author’s point that
A) pulse relaxation times can be used to identify
different tissues in the body.
B) magnetic resonance imaging is safer than other
imaging techniques.
C) infections and tumors look similar using magnetic
resonance imaging.
D) hydrogen protons behave like a small bar magnet.
10According to the table,which tissue is the first to return to its original magnetic vector resting state?
A) Water/CSF
B) Liver
C) Fat
D) Tendon
11It can reasonably be inferred from the table that
A) some tissues display axial spin relaxation times are much longer than their magnetic vector relaxation
times.
B) it generally takes longer for the magnetic vector to return to its resting state than the axial spin.
C) it often takes twice as long for the axial spin to return to its resting state than the magnetic vector.
D) it always takes at least three times as long for the magnetic vector to return to its resting state than the axial spin.

请加COCO老师(微信号:shnc_2018)
百人留学备考群,名师答疑,助教监督,分享最新资讯,领取独家资料。扫码免费加入
免费获取资料
热门搜索: 上海sat培训机构排名| 2019年SAT香港考团| 上海SAT培训| 上海SAT培训班|
免责声明
1、如转载本网原创文章,情表明出处
2、本网转载媒体稿件旨在传播更多有益信息,并不代表同意该观点,本网不承担稿件侵权行为的连带责任;
3、如本网转载稿、资料分享涉及版权等问题,请作者见稿后速与新航道联系(电话:021-64380066),我们会第一时间删除。
相关内容
热报课程
- SAT课程
| 班级名称 | 班号 | 开课时间 | 人数 | 学费 | 报名 |
|---|
全真模拟测试
SAT动态

SAT考试真题的可靠获取途径以及如何...
制作:每每





